13. Deep Reinforcement Learning Integration
Sinergym provides features to utilize Deep Reinforcement Learning algorithms from Stable Baselines 3. However, Sinergym is also compatible with any algorithm that operates with the Gymnasium interface.
Stable Baselines 3: |
|||
Algorithm |
Discrete |
Continuous |
Type |
PPO |
YES |
YES |
OnPolicyAlgorithm |
A2C |
YES |
YES |
OnPolicyAlgorithm |
DQN |
YES |
NO |
OffPolicyAlgorithm |
DDPG |
NO |
YES |
OffPolicyAlgorithm |
SAC |
NO |
YES |
OffPolicyAlgorithm |
TD3 |
NO |
YES |
OffPolicyAlgorithm |
To this end, we will refine and develop Callbacks, a set of functions that will be called at specific stages of the training procedure. Callbacks allow you to access the internal state of the RL model during training. They enable monitoring, auto-saving, model manipulation, progress bars, and more. Our callbacks inherit from Stable Baselines 3 and can be found in sinergym/sinergym/utils/callbacks.py.
The Type column is specified due to its importance in the
Stable Baselines callback functionality.
13.1. DRL Callback Logger
A callback allows us to customize our own logger for DRL Sinergym executions. Our goal is to log all information about our custom environment specifically in real-time. Each algorithm has its own nuances regarding how information is extracted, hence its implementation.
Note
You can specify if you want the Sinergym logger (see Logger) to record simulation
interactions during training simultaneously using the sinergym_logger
attribute in the constructor.
The LoggerCallback inherits from Stable Baselines 3’s BaseCallback and uses
Weights&Biases (wandb) in the background to host all extracted
information. With wandb, it’s possible to track and visualize all DRL training in real time,
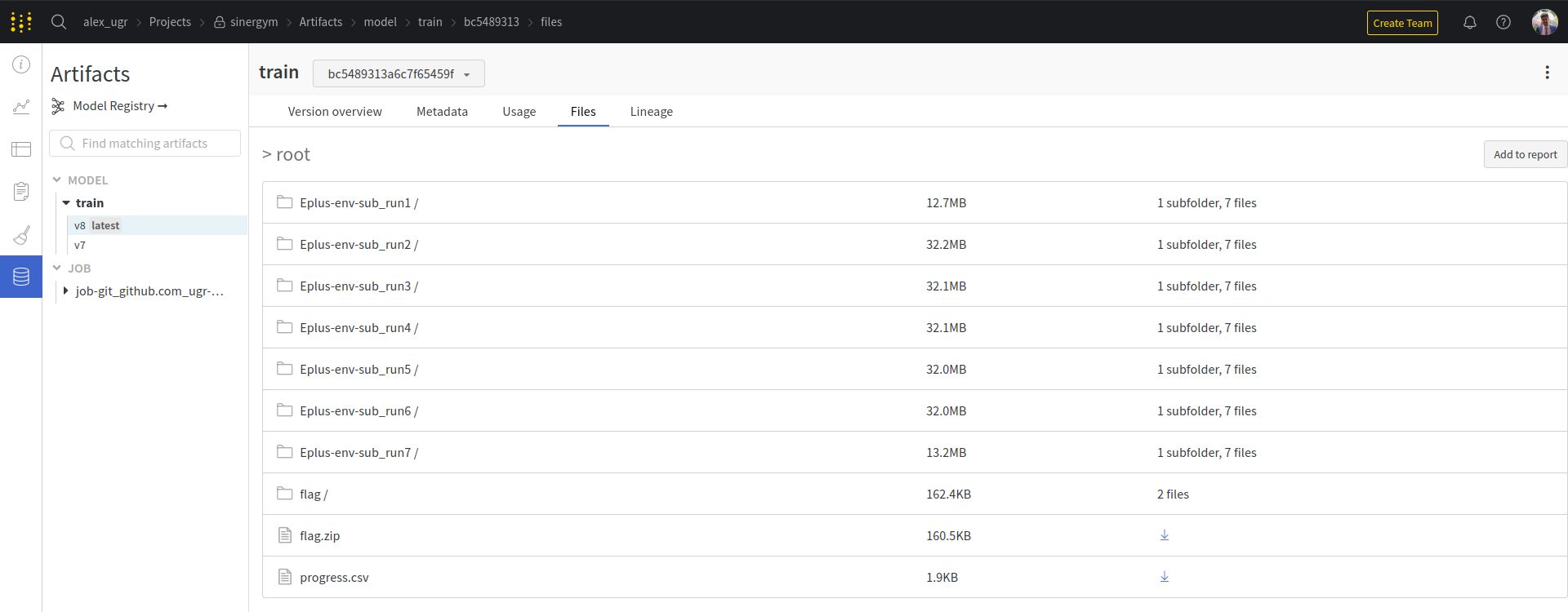
register hyperparameters and details of each execution, save artifacts such as models and Sinergym
output, and compare different executions. Here is an example:
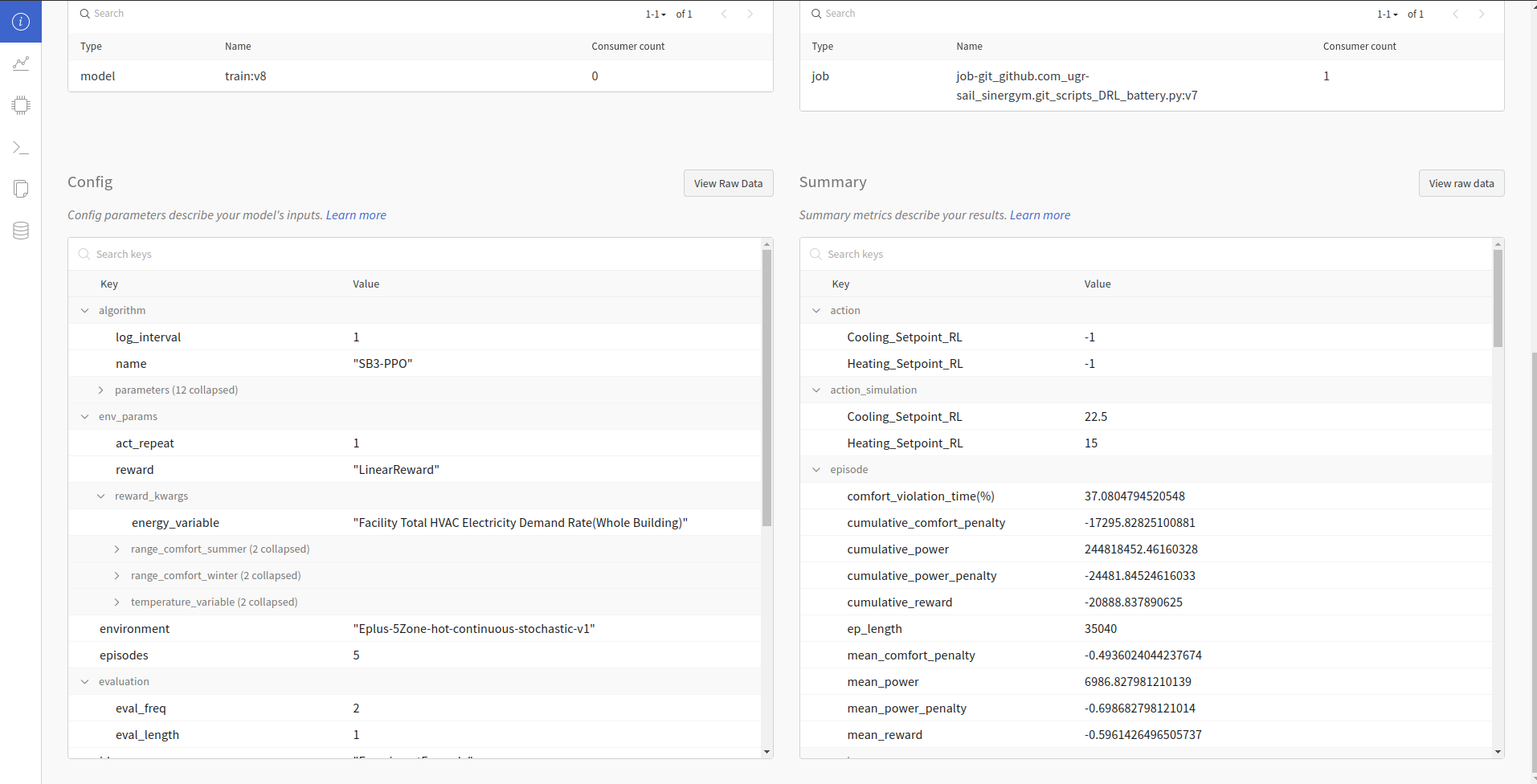
Hyperparameter and summary registration:
Artifacts registered (if evaluation is enabled, best model is registered too):
Metrics visualization in real time:
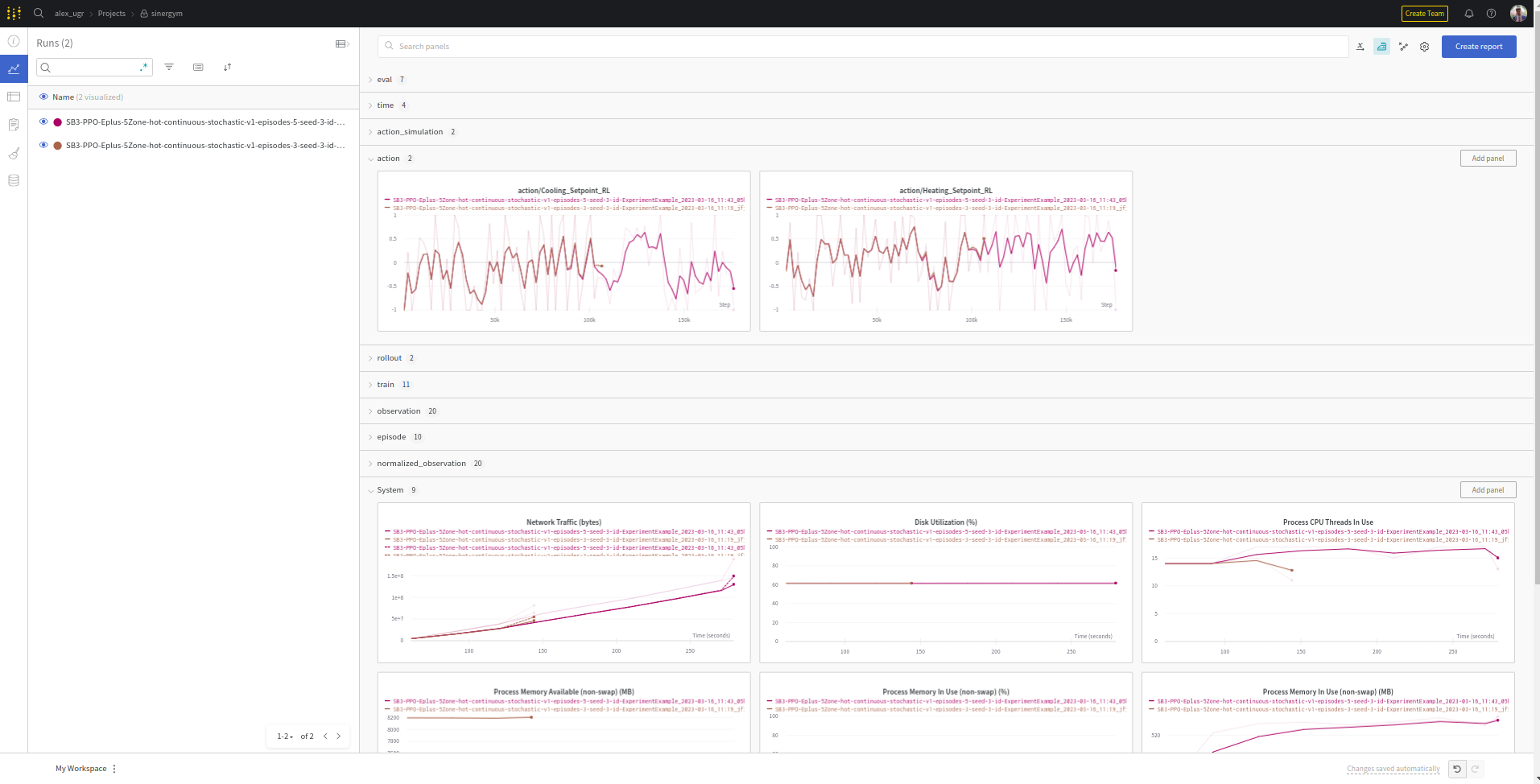
There are tables which are in some algorithms and not in others and vice versa. This depends on the algorithm used.
Note
Since version 3.0.6, Sinergym can record real-time data with the same timestep frequency regardless of the algorithm. See #363.
13.2. Evaluation Callback
An enhanced callback, named LoggerEvalCallback, is used for evaluating the model versions obtained during
the training process with Sinergym. It stores the best model obtained, not necessarily the final one from
the training process. This callback inherits from Stable Baselines 3’s EventCallback.
A key feature is that the model evaluation is logged in a specific section in wandb for the precise metrics of the building model. The evaluation is tailored for Sinergym’s specific characteristics.
In the LoggerEvalCallback constructor, we define the number of training episodes for the evaluation process.
We also specify the number of episodes for each evaluation to be performed.
More episodes lead to more accurate averages of the reward-based indicators, providing a more realistic assessment of the current model’s performance. However, this increases the time required.
The callback calculates timestep and episode averages for power consumption, temperature violation, comfort penalty, and power penalty. It also calculates the percentage of comfort violation in episodes. Currently, only the mean reward is considered when deciding if a model is better.
13.3. Weights and Biases Structure
The primary structure for Sinergym with wandb includes:
action_network: The raw output from the DRL algorithm network.
action_simulation: The transformed output used by the simulator for processing and calculating the next state and reward in Sinergym.
episode: Stores comprehensive information about each episode, equivalent to
progress.csvin Sinergym logger (Output format section). It includes:episode_num: Episode number.
episode_length: Timesteps per episode.
mean_reward: Average reward per step in the episode.
cumulative_reward: Total reward for the entire episode.
mean_power_demand: Average power demand per step in the episode.
cumulative_power_demand: Total power demand for the entire episode.
mean_temperature_violation: Average degrees temperature violation (out of comfort range) per step in the episode.
cumulative_temperature_violation: Total degrees temperature violation for the entire episode.
comfort_violation_time(%): Percentage of time the comfort range is violated in the episode (timesteps out of range).
mean_abs_energy_penalty: Average absolute energy penalty per step in the episode.
cumulative_abs_energy_penalty: Total absolute energy penalty for the entire episode.
mean_abs_comfort_penalty: Average absolute comfort penalty per step in the episode.
cumulative_abs_comfort_penalty: Total absolute comfort penalty for the entire episode.
mean_reward_energy_term: Average reward energy term per step in the episode (weighted absolute energy penalty).
cumulative_reward_energy_term: Total reward energy term for the entire episode (weighted absolute energy penalty).
mean_reward_comfort_term: Average reward comfort term per step in the episode (weighted absolute comfort penalty).
cumulative_reward_comfort_term: Total reward comfort term for the entire episode (weighted absolute comfort penalty).
observation: Records all observation values during simulation, dependent on the simulated environment (Action space section).
normalized_observation (optional): Appears only when the environment is wrapped with normalization (Wrappers section). The model trains with these normalized values, and both original and normalized observations are recorded.
rollout: Default algorithm metrics in Stable Baselines. For instance, DQN includes
exploration_rate, which is not present in other algorithms.time: Monitors execution time.
train: Records specific neural network information for each algorithm, provided by Stable Baselines and rollout.
eval: Records all evaluations conducted during training if the callback is set up. The graphs here mirror those in the episode label.
Note
Model evaluations can also be recorded by adding EvalLoggerCallback to the model learn method.
13.4. Usage
13.4.1. Model Training
Leverage this functionality for your experiments using the script sinergym/scripts/train/train_agent.py.
Key considerations for your experiments:
Models are built using an algorithm constructor, each with its own specific parameters. Defaults are used if none are defined.
If you normalize the environment wrapper, models will train in these normalized spaces.
Concatenate callbacks in a
CallbackListinstance from Stable Baselines 3.The neural network begins training upon executing the
model.learn()method, where you specifytimesteps,callbacks, andlog_interval.Curriculum Learning can be implemented by adding a model field with a valid model path. The script will load and train the model.
The train_agent.py script requires a single parameter, -conf, a string indicating the JSON
file containing all experiment details. Refer to the JSON structure in sinergym/scripts/train/train_agent_PPO.json:
Mandatory parameters: environment, episodes, algorithm (and any non-default algorithm parameters).
Optional parameters: environment parameters (overwrites default if specified), seed, pre-training model to load, experiment ID, wrappers (in order), training evaluation, wandb functionality, and cloud options.
Field names must match the example, or the experiment will fail.
The script performs the following:
Names the experiment in the format:
<algorithm>-<environment_name>-episodes<episodes_int>-seed<seed_value>(<experiment_date>)Initiates WandB experiment tracking with that name (if configured in JSON), creating a local path (./wandb).
Logs all JSON configuration parameters (including sinergym.__version__ and Python version).
Sets environment parameters if specified.
Applies specified wrappers from JSON.
Defines model algorithm with specified hyperparameters.
Calculates training timesteps from number of episodes.
Sets up evaluation callback if specified.
Sets up WandB logger callback if specified.
Trains with environment.
If remote store is specified, saves all outputs in Google Cloud Bucket. If wandb is specified, saves all outputs in wandb run artifact.
Auto-deletes remote container in Google Cloud Platform if auto-delete parameter is specified.
13.4.2. Model Loading
Use the script sinergym/scripts/eval/load_agent.py to load and evaluate or execute a previously trained model.
The load_agent.py script requires a single parameter, -conf, a string indicating the JSON file
containing all evaluation details. Refer to the JSON structure in
sinergym/scripts/eval/load_agent_example.json:
Mandatory parameters: environment, episodes, algorithm (name only), and model to load.
Optional parameters: environment parameters (overwrites default if specified), experiment ID, wrappers (in order), wandb functionality, and cloud options.
The script loads the model and predicts actions from states over the specified episodes. The information is collected and sent to remote storage (like WandB) if specified, otherwise it remains in local memory.
The model field in JSON can be a local path to the model, a bucket url in the form
gs://, or a wandb artifact path for stored models.
Note
This project is a work in progress. Direct support for additional algorithms is planned for the future!